
2025-06-10T13:54:10
Understanding Skin Grafts
- Dermatology
- Family Medicine
- Internal Medicine
- Orthopedics
July 13, 2017 | Orthopedics
Specialties:Orthopedics
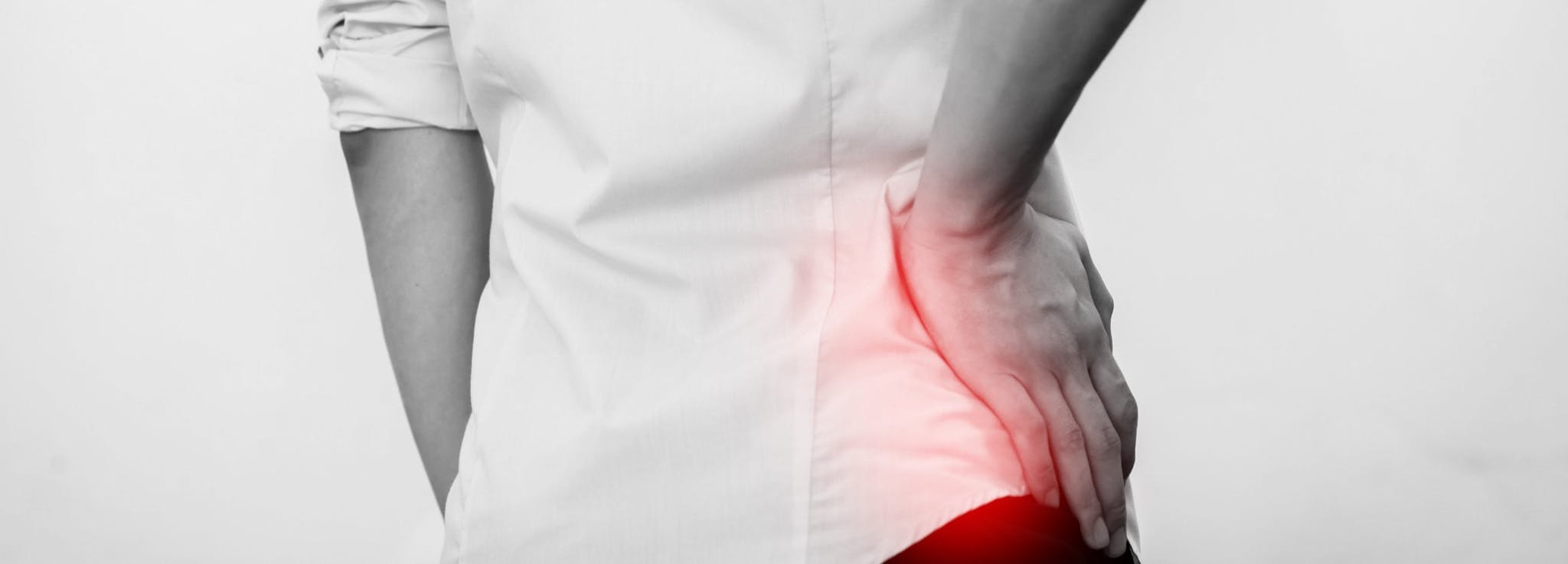
If you’ve struggled with hip pain and conservative treatment methods have been unsuccessful, hip replacement surgery may be an option. During a hip replacement, your surgeon will remove the damaged sections of the hip joint and replace them with new parts—typically made from metal, ceramic and tough plastic.
If you’re experiencing hip pain with any of the following factors, your doctor may suggest considering hip replacement surgery:
A few specific conditions can damage the hip joint and often necessitate hip replacement. These include:
Hip replacement surgery is a significant procedure, and deciding whether it’s the right time in your life to have it performed is important. When considering this choice, most people are looking at at least one of several possible factors:
Each individual case is different, and in the end, the decision will be yours and yours alone.
Many people deal with pain, swelling and stiffness for years before they consider hip replacement surgery as an option. Others only see a doctor when mechanical symptoms like buckling, clicking, grinding or limping worsen.
In cases of arthritis, this can be problematic in some cases. With worsening arthritis comes increasing stiffness in the joints, which can make hip replacement surgery more difficult to perform. This can lead to a longer recovery process, more physical therapy and, in some severe cases, a permanent loss of joint flexibility that is unable to return even after successful surgery. If you’re debating hip replacement surgery for worsening arthritis symptoms, this is a factor to keep in mind.
If you’re dealing with pain or other symptoms in the hip, speak with your doctor, who will inform you if hip replacement surgery might be a good choice for you.
“Hip replacement.” The Mayo Clinic. http://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/hip-replacement/home/ovc-20313778
“Arthritis and Hip Replacement Surgery.” WebMD. http://www.webmd.com/osteoarthritis/guide/hip-replacement-surgery#1
“Do I Need a Joint Replacement?” American Academy of Hip and Knee Surgeons. http://www.aahks.org/care-for-hips-and-knees/do-i-need-a-joint-replacement/
WRITTEN BY:
Michael Carlson, MD

2025-06-10T13:54:10

2024-06-21T14:29:51

2024-02-06T11:40:13

2023-03-30T11:23:12
This information is not intended to replace the advice of a medical professional. You should always consult your doctor before making decisions about your health.