
2024-07-12T16:54:51
Sunscreen Travel Tips
- Dermatology
July 31, 2018 | Orthopedics
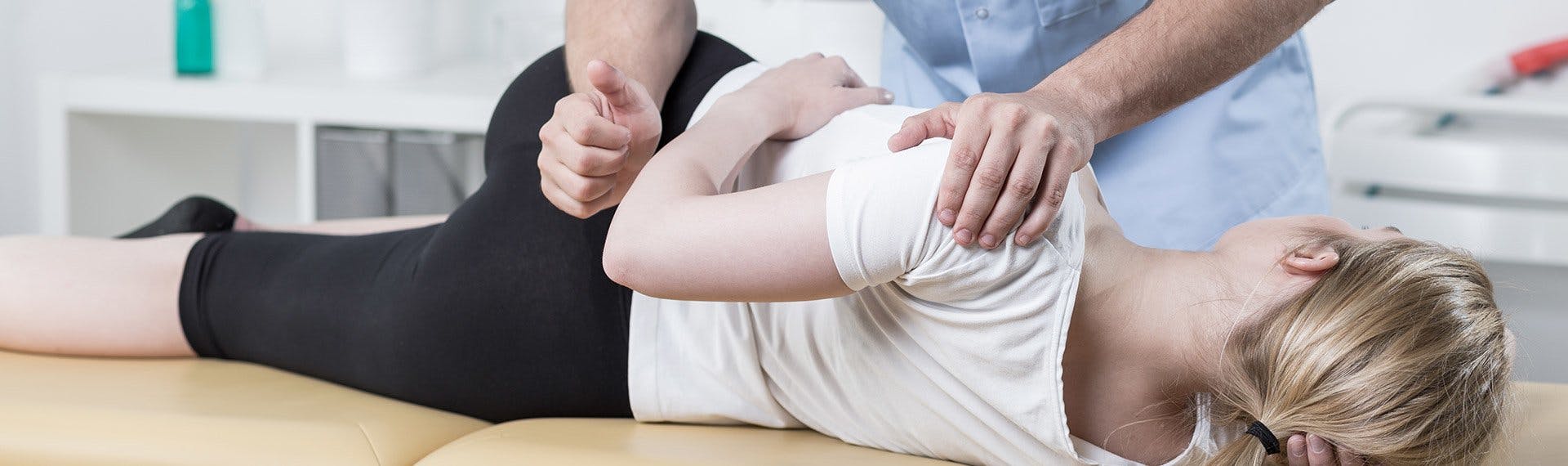
The shoulder is one of the most mobile joints in the body, but having extreme mobility puts a demand on the structure of the shoulder, which consists of three bones and a complex system of ligaments, tendons and muscles. That demand can cause the labrum to tear.
The labrum makes up part of the shoulder socket, helping the humerus bone fit deeper into the scapula. The labrum acts as a stabilizer in the shoulder, permitting range of motion while also limiting excessive motion. Injuries to the labrum cause it to tear, which causes a flap of tissue to move in and out of the joint, causing pain. A torn labrum causes the shoulder to be less stable.
A labral tear may ache for a long time after you perform certain shoulder movements. It might feel as if there’s a catching sensation in your shoulder or you may feel a sharp pop. The shoulder will probably feel loose.
A labral tear can be difficult to see, even in an MRI. You may need a CT scan using a special dye that leaks into the tear and highlights it on the scan. The surgeon may also want to look into the shoulder using an arthroscope, which is a small camera that can be inserted into the joint.
Typically, the shoulder is treated first non-surgically with rest and anti-inflammatory medications. Your orthopedist may suggest a cortisone injection to reduce the swelling and pain. Physical therapy is often prescribed to help improve the strength of your shoulder muscles, which can help stabilize the shoulder.
Most commonly, a labral tear occurs when the shoulder is subjected to trauma, but it can also occur due to repetitive shoulder motion. Traumatic injuries include:
Repetitive injuries could occur if you routinely lift weights or throw balls. If your golf club hits the ground during your swing, it could cause the labrum to tear due to the force of the strike carrying through to the arm.
For small tears, the surgeon can use an arthroscope to remove the frayed edges of the labrum, which usually gets rid of your symptoms. For larger tears, the surgeon will need to repair the labrum. Plan to wear a sling for six weeks or longer after surgery to protect the joint as it heals.
Your doctor can offer further information when it comes to labral tears.
Sources:
“Shoulder Joint Tear (Glenoid Labrum Tear.)” OrthoInfo. https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/diseases–conditions/shoulder-joint-tear-glenoid-labrum-tear/
“Labral Tears.” The Steadman Clinic and Steadman Philippon Research Institute. https://www.thesteadmanclinic.com/patient-education/shoulder/labral-tears

WRITTEN BY:
The Live Better Team


2024-07-12T16:54:51

2024-07-02T11:42:04

2024-07-01T13:49:28

2024-06-21T14:29:51
This information is not intended to replace the advice of a medical professional. You should always consult your doctor before making decisions about your health.