
2024-07-12T16:54:51
Sunscreen Travel Tips
- Dermatology
May 20, 2019 | Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation
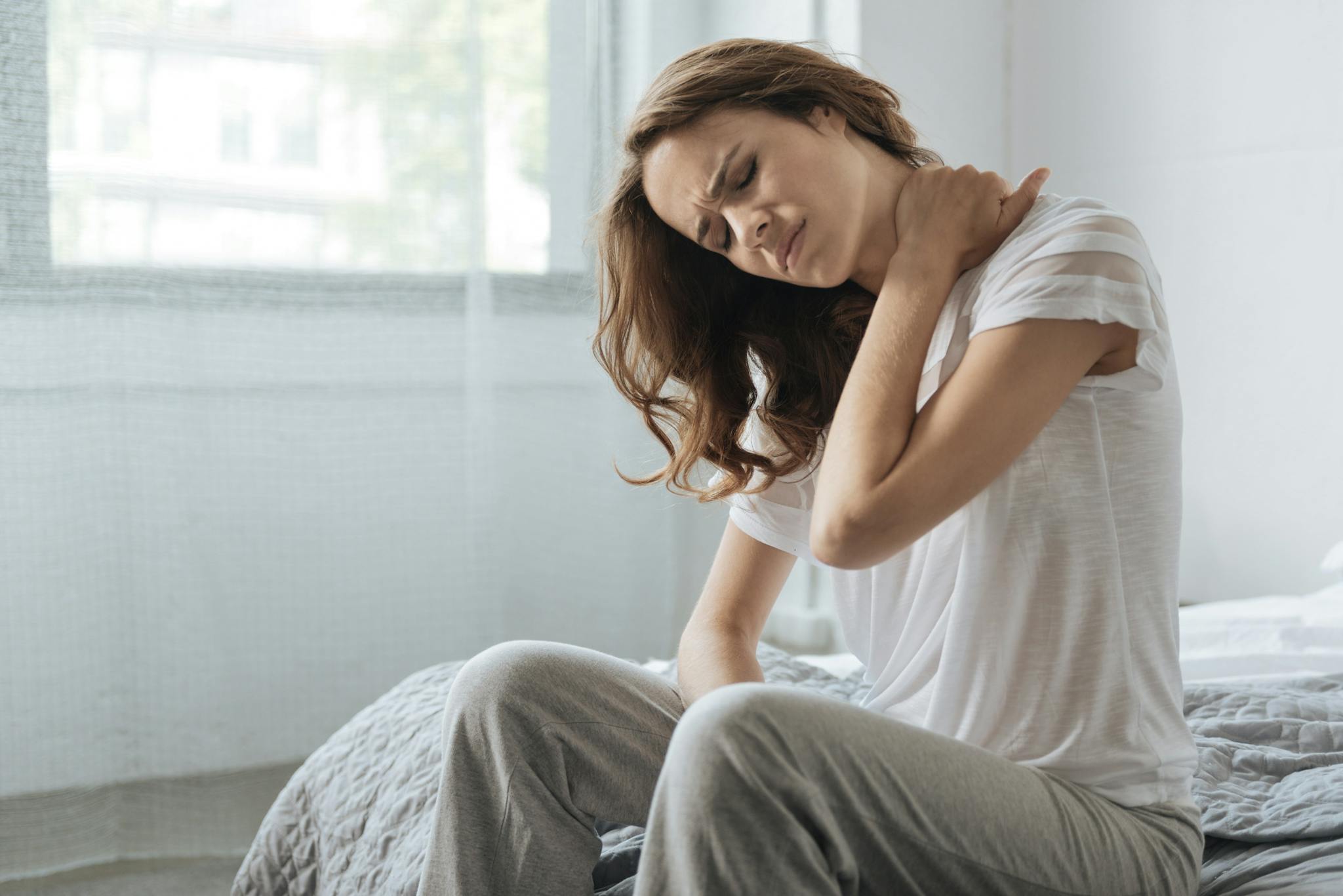

Also called a neck strain or neck sprain, whiplash is a soft tissue injury to the neck. The damage is caused by a sudden, forceful, back-and-forth movement of the neck. This injury is usually a result of a car accident but can also result from a sports accident or other trauma. Whiplash can also include injury to the joints, discs, ligaments, nerves and tendons in the neck.
Signs and symptoms of whiplash most often appear within 24 hours of the injury, though they can appear later. Symptoms of whiplash include:
Whiplash is diagnosed in a variety of ways. You may need to get a physical exam, X-ray, MRI or CT scan.
The treatment for whiplash depends on the severity of the injury and the treatments focus on pain management and restoring normal range of motion in your neck. Treatments for pain management may include rest, applying heat or cold, over-the-counter or prescription pain medications and muscle relaxants. Treatments for restoring range of motion may include prescribed stretching and movement exercises or physical therapy.
Most people with a whiplash injury recover in a few weeks but it could take a few months. Some do experience persistent pain for several months or longer.
If you experience pain or other symptoms after a car accident or similar trauma you should see your healthcare provider.
WRITTEN BY:
The Live Better Team


2024-07-12T16:54:51

2024-07-02T11:42:04

2024-07-01T13:49:28

2024-06-21T14:29:51
This information is not intended to replace the advice of a medical professional. You should always consult your doctor before making decisions about your health.